health and remedies
Premature infants in neonatal care facilities are vulnerable to deadly diseases, according to a study.
The birth of a premature infant is a complex and challenging experience for both parents and healthcare providers. These tiny, fragile beings often require intensive medical care in neonatal care facilities, also known as neonatal intensive care units (NICUs). While these units play a crucial role in saving the lives of premature babies, a recent study has shed light on the vulnerability of these infants to deadly diseases during their stay in NICUs.
The Premature Birth Crisis
Premature birth, defined as birth before 37 weeks of pregnancy, is a global health issue affecting millions of infants each year. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 15 million babies are born prematurely annually. These premature births can occur due to various factors, including maternal health, multiple pregnancies (e.g., twins or triplets), and medical conditions affecting the mother.
Neonatal Care: A Lifesaving Haven
Neonatal care facilities, equipped with specialized medical equipment and a skilled healthcare team, provide premature infants with the necessary care and support for survival. These facilities are designed to address the unique needs of these tiny patients, offering interventions such as respiratory support, intravenous nutrition, and monitoring for potential complications.
Vulnerability to Deadly Diseases
Despite the critical role played by neonatal care facilities, a recent study has highlighted the vulnerability of premature infants to deadly diseases during their stay in NICUs. These infants often have underdeveloped immune systems, making them more susceptible to infections and other medical complications.
Several factors contribute to the increased risk of deadly diseases among premature infants in NICUs:
- Invasive Procedures: Premature infants may require invasive medical procedures, such as intubation or the insertion of central lines, which can introduce infection-causing pathogens.
- Close Proximity: The close proximity of infants in NICUs can facilitate the spread of infections among vulnerable patients.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Premature infants may have underlying health conditions that further weaken their immune systems.
- Limited Vaccination: Premature infants often cannot receive routine vaccinations until they reach a certain age, leaving them susceptible to vaccine-preventable diseases.
Preventive Measures and Awareness
To mitigate the risks faced by premature infants in neonatal care facilities, healthcare providers and parents must work together to implement preventive measures:
- Strict Hand Hygiene: Healthcare providers should practice meticulous hand hygiene to reduce the transmission of pathogens.
- Isolation Protocols: Infants with contagious diseases should be isolated to prevent the spread of infections in NICUs.
- Parent Education: Parents should be educated about the importance of hand hygiene and infection prevention measures when visiting their premature infants.
- Vaccination: Ensuring that healthcare providers and parents are up-to-date on vaccinations can reduce the risk of vaccine-preventable diseases.
Neonatal care facilities are essential for the survival of premature infants, but they also pose challenges in terms of infection control and disease prevention. The vulnerability of these tiny patients underscores the importance of rigorous infection prevention protocols and heightened awareness among healthcare providers and parents.
As medical research continues to advance, it is hoped that new strategies and treatments will emerge to further protect premature infants during their critical period of development in neonatal care facilities. In the meantime, a collective effort is required to ensure that these vulnerable infants receive the best possible care and protection against deadly diseases.
Group Media Publications
Entertainment News Platforms – anyflix.in
Construction Infrastructure and Mining News Platform – https://cimreviews.com/
General News Platform – https://ihtlive.com/
Podcast Platforms – https://anyfm.in
Trending
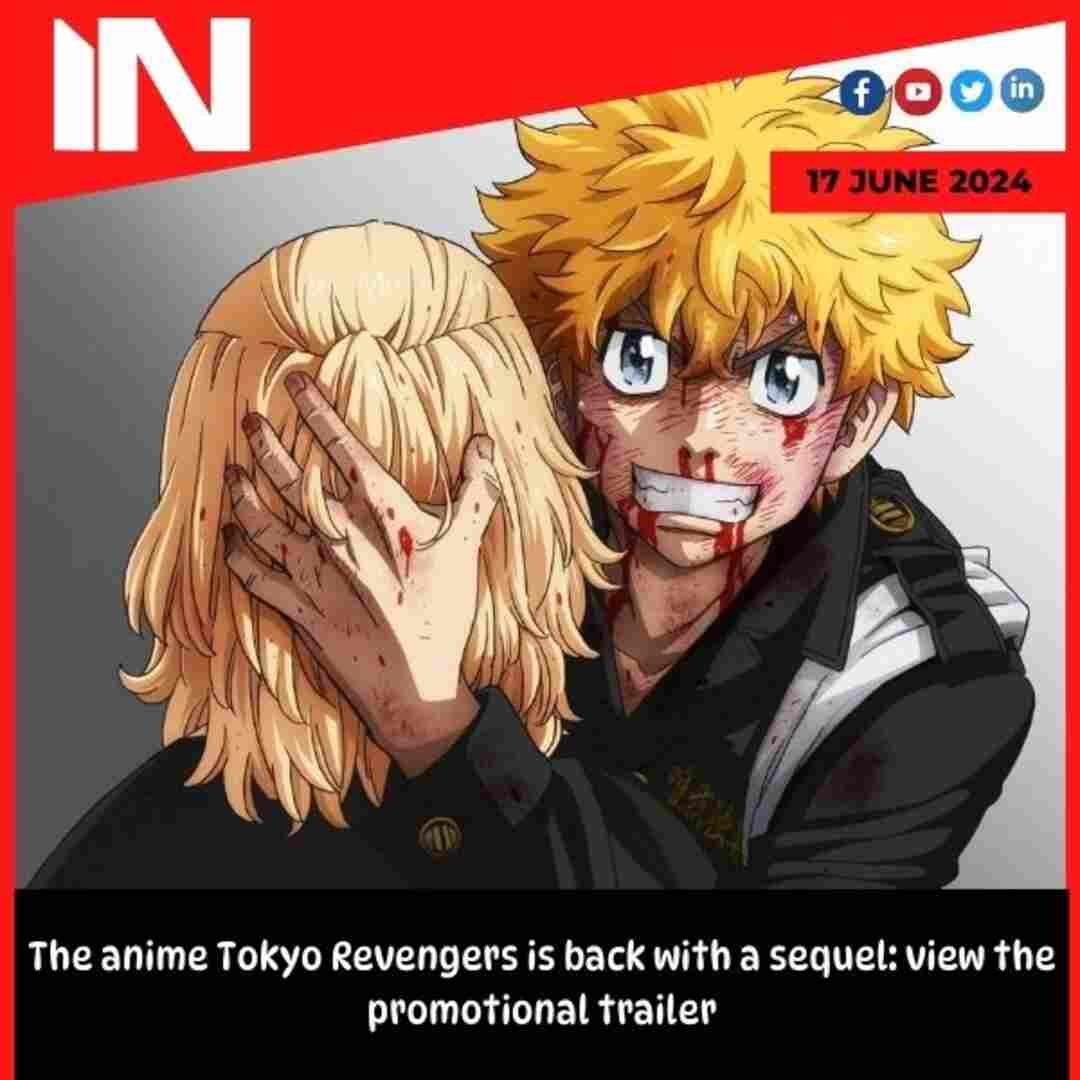
Holi 2024: Inside, professional advice on overcoming a Bhang hangover

Holi 2024: We are eagerly awaiting the arrival of this festival of colors, which is quickly approaching. Every year, the nation celebrates Holi with great fanfare and extravagance. Holi commemorates the eternal love and marriage of Goddess Radha and Lord Krishna. In addition, Holi commemorates Lord Vishnu’s victory over Hiranyakashipu, highlighting the idea that good always triumphs over evil. Holi will be celebrated on March 25 this year. Holika Dahan, also known as Chhoti Holi, is observed the day before Holi. On the day of Holi, many customs and rites are observed throughout India. The cities of Barnsana and Nandgaon celebrate Lathmar Holi, whereas Vrindavan celebrates Phoolwali Holi.
Holi 2024: Here are some professional suggestions to avoid Bhang hangover, ranging from eating a balanced diet to sipping herbal tea.
During Holi, a variety of snacks and beverages are made to be enjoyed with loved ones. The colorful, crispy, and delectable Holi snacks range from gujia to rasmalai to namakpare. Thandai, a delightful concoction of milk, spices, and sweets, is the queen of the drink table. Bhang is among the primary draws of Holi. For its euphoric impact, thandai is sometimes blended with powdered paste made from the female cannabis plant’s leaves and flowers. But after the first euphoria wears off, there’s also the inevitable hangover the following morning.
Methods for overcoming a hangover
Hydrate the body: Hydration is crucial for managing a hangover caused by Bhang during Holi. Sip on lots of water to flush out toxins and replenish your body’s moisture.
Consume coconut water: Coconut water and other electrolyte-rich beverages can help replenish lost nutrients.
A balanced diet: blood sugar regulation and nausea reduction can be achieved by eating a well-balanced meal high in carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats.
Herbal teas and rest: Herbal teas with relaxing properties, such as peppermint or ginger, can ease stomach discomfort. Your body can mend itself by resting in a quiet, dark environment.
Limit alcohol intake: Limit your alcohol and cannabis intake to prevent symptoms from getting worse. As soon as symptoms develop or continue, get medical help.
Group Media Publications
Entertainment News Platforms – anyflix.in
Construction Infrastructure and Mining News Platform – https://cimreviews.com/
General News Platform – https://ihtlive.com/
Podcast Platforms – https://anyfm.in
-
 Music2 months ago
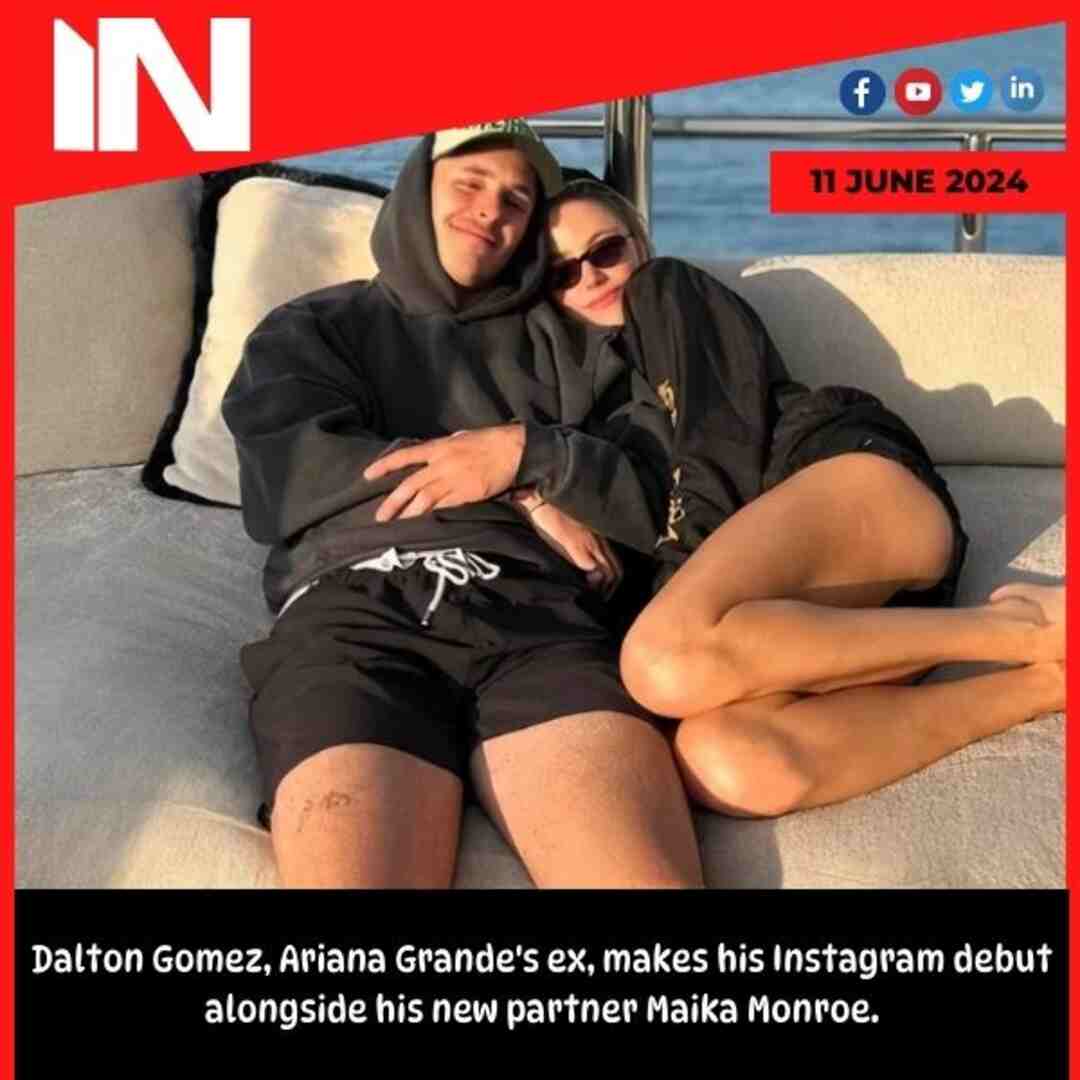
Music2 months agoDalton Gomez, Ariana Grande’s ex, makes his Instagram debut alongside his new partner Maika Monroe.
-

 Web Series1 month ago
Web Series1 month agoSpoilers for Star Wars: The Acolyte, episode three: The new episode has caused the internet to go crazy.
-

 Music2 months ago
Music2 months agoMin Hee-jin will continue to serve as ADOR’s CEO, and following the shareholders’ meeting, HYBE names three new board members.
-
 Entertainment2 months ago
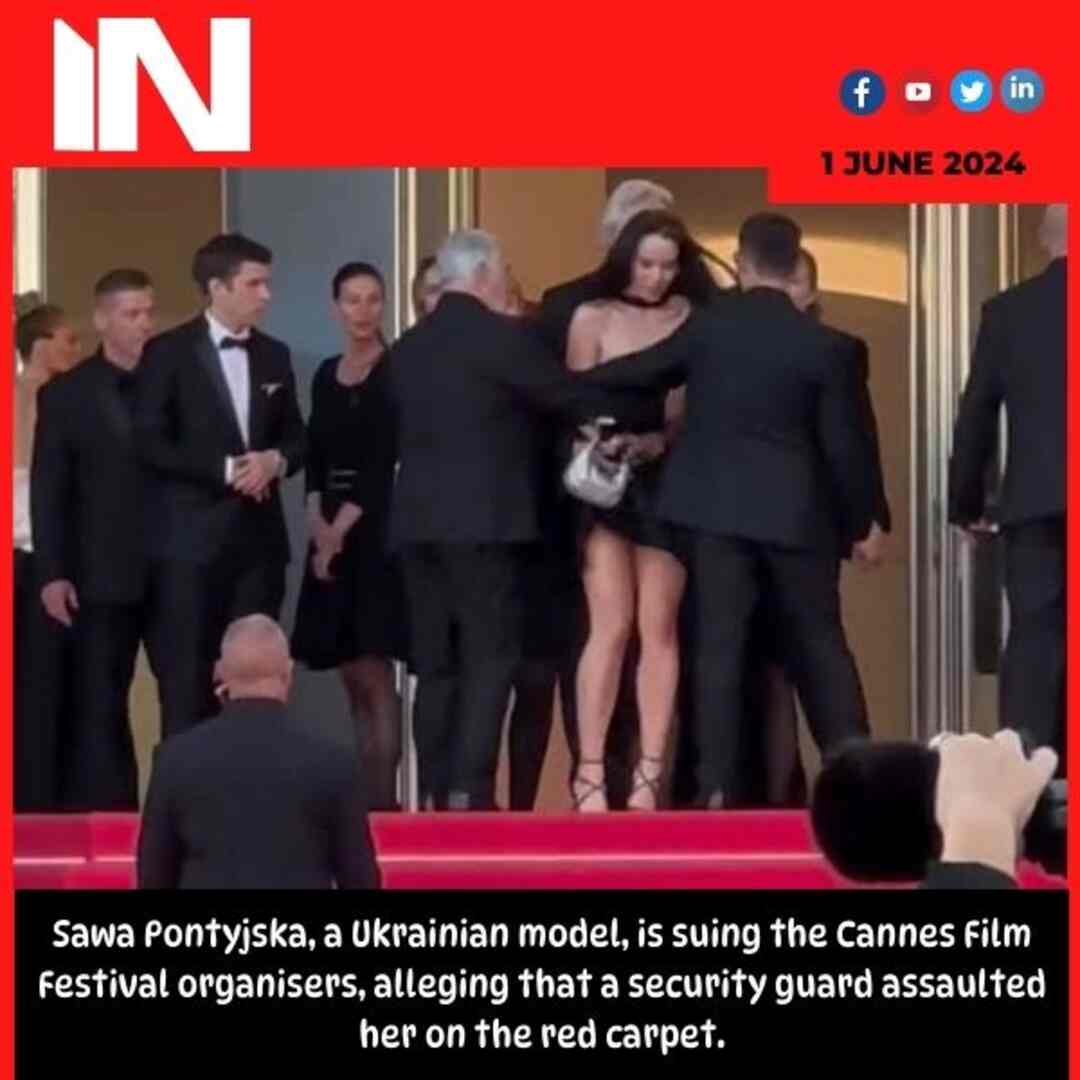
Entertainment2 months agoSawa Pontyjska, a Ukrainian model, is suing the Cannes Film Festival organisers, alleging that a security guard assaulted her on the red carpet.
-

 Hollywood1 month ago
Hollywood1 month agoDeadpool and Wolverine might shatter box office records, which would be unprecedented for an R-rated film.
-
 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoKai Cenat, a Twitch celebrity, travels to Taiwan for this poignant occasion.
-

 Music1 month ago
Music1 month agoBianca Censori’s obscene Tokyo ensemble provokes indignation in Japan. while Kanye West flies economy after losing…
-

 Hollywood2 months ago
Hollywood2 months agoMovie Review: ‘Am I OK?’ is a charming comedy about friendship that features Dakota Johnson’s endearing genuineness.