health and remedies
Heart disease and soil contamination are related, according to research

Pesticides and heavy metals in soil may have detrimental effects on the cardiovascular system, according to a review research.
According to the author Professor Thomas Munzel of the University Medical Center Mainz in Germany, “Soil contamination is a less evident hazard to human health than filthy air.” But there is growing evidence that soil pollutants may harm cardiovascular health through a variety of ways, including as inflammation and tampering with the body’s internal clock.
At least nine million deaths occur annually as a result of air, water, and soil pollution. Cardiovascular diseases include chronic ischemic heart disease, heart attacks, strokes, and irregular heartbeats account for more than 60% of pollution-related illness and fatalities (arrhythmias).
In this essay, the connections between soil contamination and human health are discussed, with an emphasis on cardiovascular disease. Heavy metals, herbicides, and plastics are examples of soil contaminants. According to the authors, contaminated soil may cause cardiovascular disease by generating inflammation, upsetting the biological clock, and raising oxidative stress in blood vessels (with more “bad” free radicals and fewer “good” antioxidants) (circadian rhythm).
By breathing in dust from the desert, crystals from fertiliser, or plastic particles, dirty soil can enter the body. Plastics, organic toxicants (such as those found in pesticides), heavy metals like cadmium and lead, and toxic organic substances can all be ingested orally. Rivers become tainted with soil pollutants that can be absorbed when consumed.
An increased risk of cardiovascular disease has been associated with pesticide use. The entire public may consume pesticides from tainted food, soil, or water, while workers in the chemical and agricultural industries are more likely to be exposed to them.
A heavy metal called cadmium can be found in minute levels naturally in the air, water, soil, and food as well as being derived from industrial and agricultural sources. For non-smokers, food is the main source of cadmium. The article mentions a Korean study that found middle-aged Koreans with high blood cadmium had raised risks of stroke and hypertension and notes that population studies on the association between cadmium and cardiovascular disease have produced conflicting results.
Because of its natural toxicity, lead can pollute the environment whether it is mined, smelted, manufactured, or recycled. High blood lead levels have been linked to cardiovascular disease, including coronary heart disease, heart attacks, and stroke in women and diabetics, according to studies. Additional research has shown that exposure to arsenic, a naturally occurring metalloid whose levels can rise as a result of industrial activities and the use of contaminated water for crop irrigation, is linked to an increased risk of mortality from cardiovascular disease.
“Although soil pollution with heavy metals and its association with cardiovascular diseases is particularly a problem for low- and middle-income countries because their populations are exposed to these environmental pollutants in disproportionately high amounts, it becomes a problem for any country in the world due to the increasing globalisation of food supply chains and uptake of these heavy metals with fruits, vegetables, and meat,” the paper states.
It is observed that contaminated airborne dust may be hazardous. Desert dust can travel great distances, and studies have found a link between particles from Chinese and Mongolian soil and a higher risk of heart attacks in Japan. In Japan, the number of visits to the emergency department for cardiovascular conditions increased by 21% on days with high levels of Asian dust exposure.
Since nano- and microplastics can enter the bloodstream, it is conceivable that they could travel to the organs and induce systemic inflammation and cardiometabolic disease even though population studies on the impact of these materials on human cardiovascular health are lacking.
Prof. Munzel stated: “Since we are rarely exposed to a single hazardous agent, more research is required to determine the cumulative impact of numerous soil contaminants on cardiovascular disease. It is absolutely necessary to conduct research on how nano- and microplastics may cause and aggravate cardiovascular disease. In the meanwhile, it appears prudent to buy food grown in good soil, filter water to remove toxins, and wear a face mask to reduce exposure to wind-blown dust.”
Group Media Publications
Entertainment News Platforms – anyflix.in
Construction Infrastructure and Mining News Platform – https://cimreviews.com/
General News Platform – https://ihtlive.com/
Legal and Laws News Platforms – https://legalmatters.in/
Podcast Platforms – https://anyfm.in/
Trending
Holi 2024: Inside, professional advice on overcoming a Bhang hangover

Holi 2024: We are eagerly awaiting the arrival of this festival of colors, which is quickly approaching. Every year, the nation celebrates Holi with great fanfare and extravagance. Holi commemorates the eternal love and marriage of Goddess Radha and Lord Krishna. In addition, Holi commemorates Lord Vishnu’s victory over Hiranyakashipu, highlighting the idea that good always triumphs over evil. Holi will be celebrated on March 25 this year. Holika Dahan, also known as Chhoti Holi, is observed the day before Holi. On the day of Holi, many customs and rites are observed throughout India. The cities of Barnsana and Nandgaon celebrate Lathmar Holi, whereas Vrindavan celebrates Phoolwali Holi.
Holi 2024: Here are some professional suggestions to avoid Bhang hangover, ranging from eating a balanced diet to sipping herbal tea.
During Holi, a variety of snacks and beverages are made to be enjoyed with loved ones. The colorful, crispy, and delectable Holi snacks range from gujia to rasmalai to namakpare. Thandai, a delightful concoction of milk, spices, and sweets, is the queen of the drink table. Bhang is among the primary draws of Holi. For its euphoric impact, thandai is sometimes blended with powdered paste made from the female cannabis plant’s leaves and flowers. But after the first euphoria wears off, there’s also the inevitable hangover the following morning.
Methods for overcoming a hangover
Hydrate the body: Hydration is crucial for managing a hangover caused by Bhang during Holi. Sip on lots of water to flush out toxins and replenish your body’s moisture.
Consume coconut water: Coconut water and other electrolyte-rich beverages can help replenish lost nutrients.
A balanced diet: blood sugar regulation and nausea reduction can be achieved by eating a well-balanced meal high in carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats.
Herbal teas and rest: Herbal teas with relaxing properties, such as peppermint or ginger, can ease stomach discomfort. Your body can mend itself by resting in a quiet, dark environment.
Limit alcohol intake: Limit your alcohol and cannabis intake to prevent symptoms from getting worse. As soon as symptoms develop or continue, get medical help.
Group Media Publications
Entertainment News Platforms – anyflix.in
Construction Infrastructure and Mining News Platform – https://cimreviews.com/
General News Platform – https://ihtlive.com/
Podcast Platforms – https://anyfm.in
-
 Music2 months ago
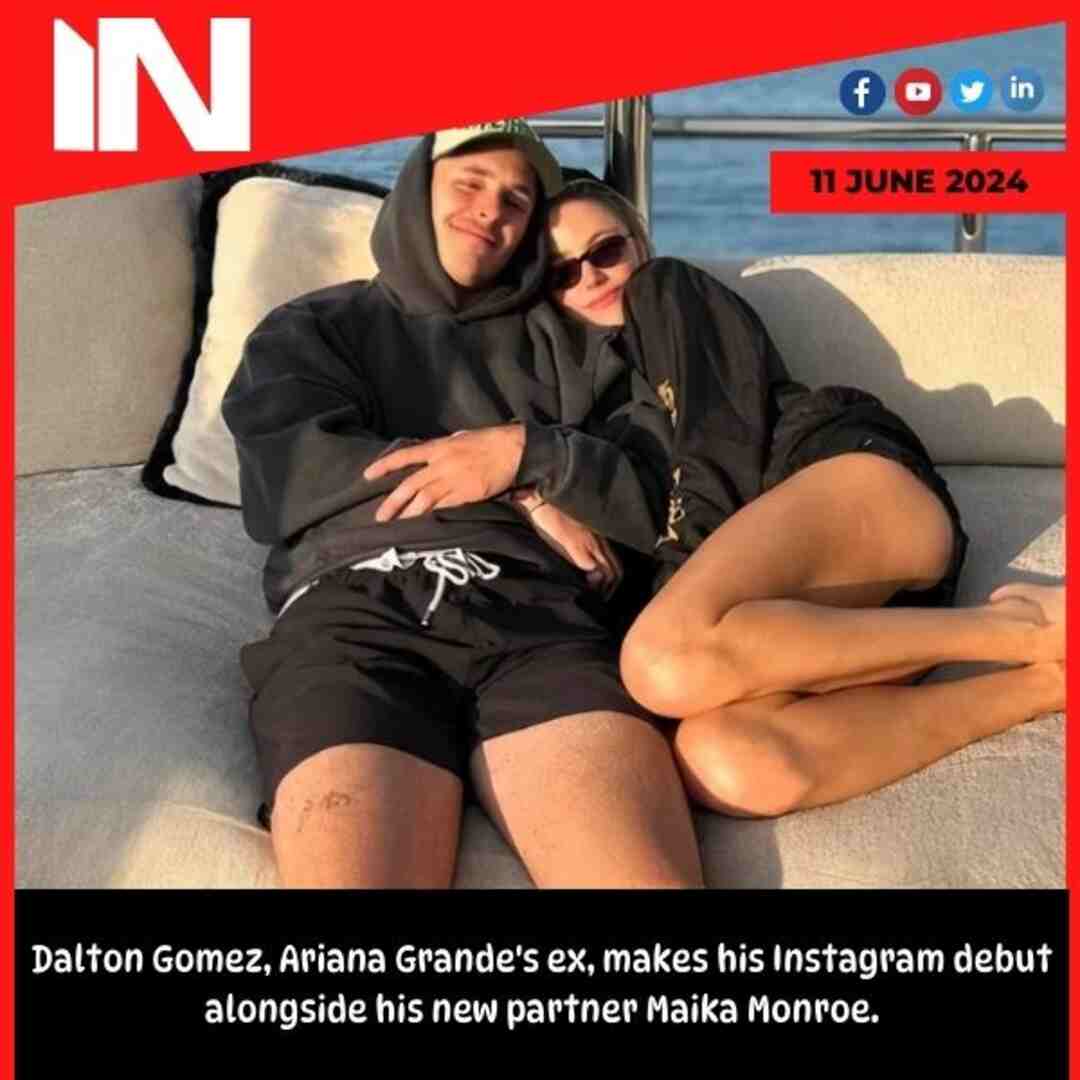
Music2 months agoDalton Gomez, Ariana Grande’s ex, makes his Instagram debut alongside his new partner Maika Monroe.
-

 Web Series2 months ago
Web Series2 months agoSpoilers for Star Wars: The Acolyte, episode three: The new episode has caused the internet to go crazy.
-

 Music2 months ago
Music2 months agoMin Hee-jin will continue to serve as ADOR’s CEO, and following the shareholders’ meeting, HYBE names three new board members.
-
 Entertainment2 months ago
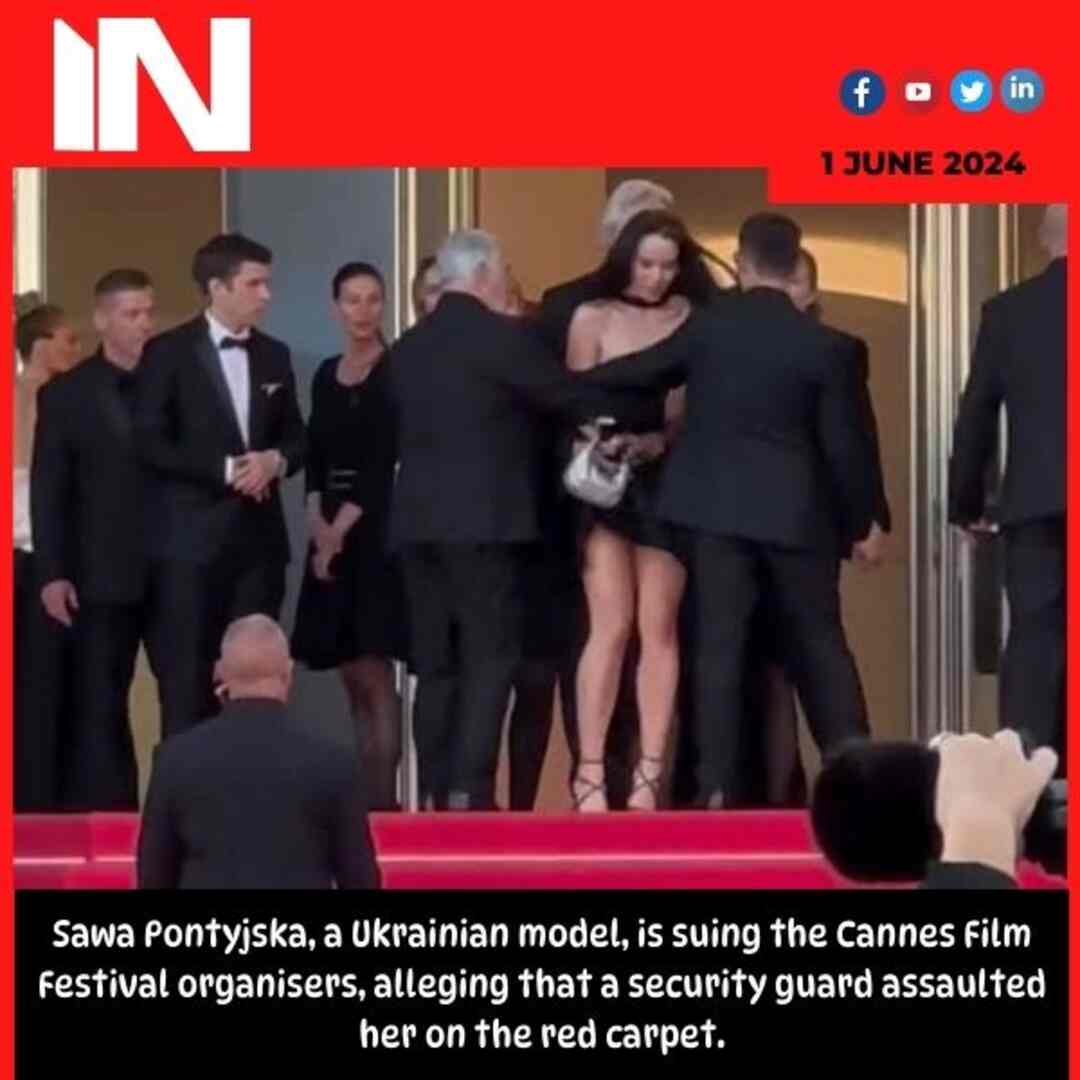
Entertainment2 months agoSawa Pontyjska, a Ukrainian model, is suing the Cannes Film Festival organisers, alleging that a security guard assaulted her on the red carpet.
-

 Hollywood1 month ago
Hollywood1 month agoDeadpool and Wolverine might shatter box office records, which would be unprecedented for an R-rated film.
-
 Entertainment2 months ago
Entertainment2 months agoKai Cenat, a Twitch celebrity, travels to Taiwan for this poignant occasion.
-

 Hollywood2 months ago
Hollywood2 months agoMovie Review: ‘Am I OK?’ is a charming comedy about friendship that features Dakota Johnson’s endearing genuineness.
-

 Music1 month ago
Music1 month agoBianca Censori’s obscene Tokyo ensemble provokes indignation in Japan. while Kanye West flies economy after losing…